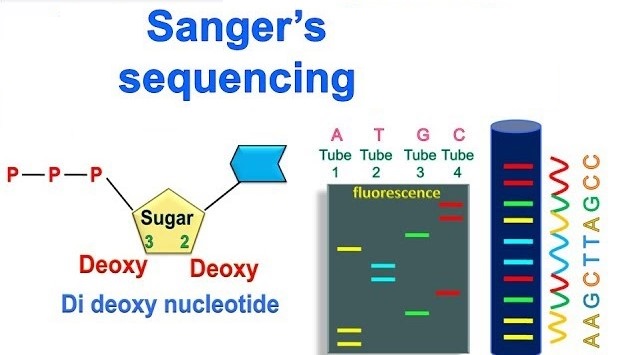
DNA sequencing is the process by which the precise order of nucleotides in a segment of DNA can be determined. Different techniques for sequencing were developed Sanger sequencing method is most widely used.The ‘Sanger’, ‘dideoxy’, or ‘chain-termination’ method of DNA sequencing relies on the enzymatic synthesis of DNA in vitro in the presence of chain-terminating inhibitors. The first step in a chain termination sequencing experiment is to anneal a short oligonucleotide primer on to target DNA to be sequenced.
In a dye terminator sequencing reaction, along with usual deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), there are four fluorescent dye-labelled dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs which emits light at a different wavelength when excited by a laser. When a ddNTP is incorporated into the growing DNA strand, synthesis is terminated due to the absence of a hydroxyl group. The final products of the sequencing reaction consist of a set of fragments which differ by only one base pair. During capillary electrophoresis, the extension products of the cycle sequencing reaction enter the capillary as a result of electro kinetic injection. A high voltage charge applied to the buffered sequencing reaction forces the negatively charged fragments into the capillaries. The extension products are separated by size based on their total charge. Shortly before reaching the positive electrode, the fluorescently labeled DNA fragments, separated by size, move across the path of a laser beam. The laser beam causes the dyes on the fragments to fluoresce. An optical detection device genetic analyzers detects the fluorescence. The Data Collection Software converts the fluorescence signal to digital data, then records the data. Because each dye emits light at a different wavelength when excited by the laser, all four colors, and therefore all four bases, can be detected and distinguished in one capillary injection.
Sanger sequencing supports a wide range of DNA sequencing applications such as
1. Sequencing of specific genes.
2. SNP identification & validation.
3. MIcrosatelite analysis.
4. Denovo sequencing etc
Available Equipment
| Make | Model | Date of installation | Status | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applied Biosystems | Genetic Analyser, AB 3130xl 628T0040 |
2006 | Working | NIV unit, Mumbai |
| Applied Biosystems | DNA Analyzer 3730 | 2014 | Working | NIV unit, Mumbai |
| Applied Biosystems | Genetic Analyser, AB 3130xl | 2007 | NIV, Pashan,Pune | |
| Applied Biosystems | Genetic Analyser, AB 3130xl | 2007 | Working | NIV Pune |